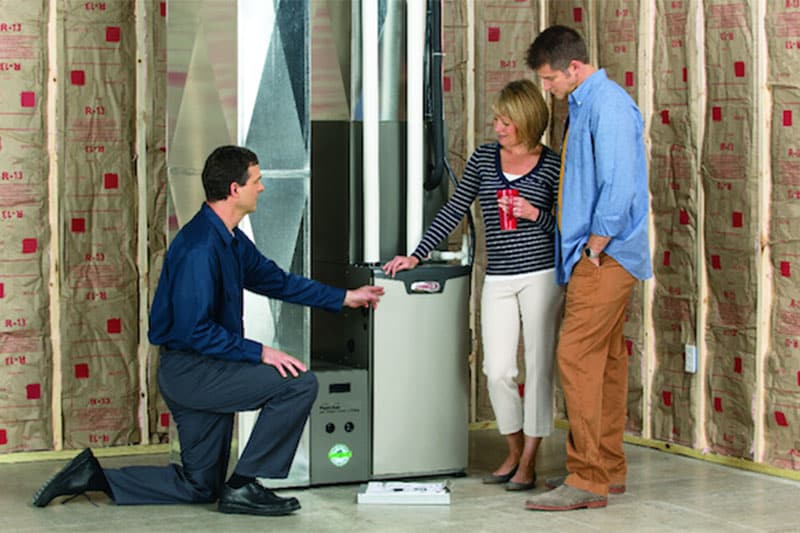
Did you know that more than half of your home’s energy costs are needed for your heating and cooling? This is the reason why it’s so important to have an energy-efficient HVAC system.
Furnace efficiency standards were last updated to an Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating of 80% in 2015. This rating system illustrates how effective your furnace is at converting natural gas into heat. An AFUE rating of 80% means your furnace will waste about 20% of the fuel it uses while generating heat.
In 2022, President Biden revealed new energy-efficiency standards for residential gas furnaces that would substantially lower emissions, save consumers money and encourage sustainability.
These revised standards are projected to:
- Save Americans $1.9 billion annually.
- Cut carbon emissions by 373 million metric tons and methane emissions by 5.1 million tons over three decades, the equivalent of what 61 million homes emit annually.
Starting in 2029, the updated rule would demand all new gas furnaces to feature AFUE ratings of 95%. This means furnaces would turn nearly 100% of the gas into usable heat.
Considering these guidelines, you might be asking yourself what does that mean for my existing furnace? Currently, next to nothing, as the proposed rule won’t go into effect until 2029 at the earliest and doesn’t affect furnaces that are already in use.
But if your furnace is nearing the end of its life and a replacement is needed in soon, highly energy-efficient furnaces are now available. Learn how these furnaces can lower your monthly energy bills.
Guide to Condensing Furnaces
How Condensing Furnaces Work
A condensing furnace is a kind of heating system that uses a secondary heat exchanger to collect wasted heat from the furnace’s exhaust gases. This limits the amount of energy wasted, enhances energy efficiency and lowers greenhouse gas emissions. It also requires less natural gas to create the same volume of heat when comparing one to other types of furnaces.
How Condensing Furnaces Differ from Non-Condensing Furnaces
The main difference between a condensing furnace and a non-condensing furnace is condensing models use a secondary heat exchanger to capture any wasted heat from its exhaust gases, while the other does not.
Expected Longevity of a Condensing Furnace
The life span of a condensing furnace depends on the brand, model and other factors. Generally speaking, a condensing furnace will last between 10-20 years with appropriate maintenance and regular service. If you don’t schedule routine maintenance, the unit may not last as long.
Why Condensing Furnaces Cost More
For the most part, condensing furnaces are more expensive than non-condensing furnaces. This is partially for their increased efficiency and the additional components needed to capture any wasted heat from its exhaust gases. However, the additional energy savings can frequently cover the cost of purchase. So ultimately, it may be more cost efficient to consider investing in a condensing furnace.
Guide to Variable-Speed Furnaces
Variable-Speed Furnaces: What They Are and How They Work
A variable-speed furnace can fine-tune its fan speed to better meet the heating needs of your home. It runs at a slower speed until it senses a drop in temperature and then speeds up to produce more heat. This [precise fan is much more efficient than traditional furnaces, as it only uses the minimum amount of energy necessary to heat your home, saving you money in the long run.
Most variable-speed furnaces are condensing furnaces, although a handful are available in non-condensing models with lower AFUE ratings. If a manufacturer wants a furnace to be classified as a condensing furnace, it must offer an AFUE rating of 90% or higher.
Do Variable-Speed Furnaces Run Constantly?
A variable-speed furnace doesn’t run all the time. Instead, it runs at different speeds according to the temperature in your South Beloit and Belvidere home as well as the amount of energy it needs to sustain that temperature.
When sufficient energy is needed to maintain your preferred temperature level, the furnace will increase to a higher speed to handle the demand. Doing this will ensure more efficient heating in your home while also providing quieter operation.
Guide to Two-Stage Furnaces
Two-Stage Furnaces: What They Are and How They Work
A two-stage furnace is a type of heating system that utilizes two different stages of operation — high and low. When set to the low stage, the furnace runs at a reduced capacity to help maintain the desired temperature for your home more efficiently. During the high stage, the furnace will instead run at maximum capacity to satisfy demands for greater heat. With a two-stage furnace, you can maintain enhanced energy efficiency and consistent temperatures throughout your home.
While two-stage furnaces are exceptionally efficient, not all all models are condensing furnaces.
Does a Two-Stage Furnace Function All the Time?
A two-stage furnace does not stay on indefinitely. In the low stage of operation, the furnace runs at reduced capacity in order to retain a preferred temperature more efficiently within your home. When more energy is needed to sustain the set temperature, the furnace will switch to its high stage and runs at full capacity. For this reason, two-stage furnaces are proven to help reduce energy costs without operating constantly.
Comparing Two-Stage and Variable-Speed Furnaces
Two-stage furnaces have two stages of functionality, low and high. During the low stage, the furnace runs at reduced capacity in order to sustain a desired temperature within your home. When a greater demand for warmth or cooling is necessary, the furnace will shift to its high stage and operate at maximum capacity.
Variable-speed furnaces, meanwhile, can function at a variety of speeds in order to maintain a comfortable temperature at home. As such, variable-speed furnaces offer greater savings on your utility bills .
Differences Between One- and Two-Stage Furnaces
One-stage furnaces have a single stage of operation and operate either at full capacity or not at all. This translates to higher energy bills because the furnace runs constantly in order to maintain a desired level of comfort at home.
Two-stage furnaces, by comparison, have two stages of operation, low and high. While in the low stage, the furnace runs at lower capacity in order to maintain the desired temperature more efficiently. When additional warmth or cooling is necessary, the furnace will change over to its high stage and operate at full capacity.
Make Your Furnace Installation Appointment with Fleming Heating & Air Conditioning Inc Today
Modern furnace technology can be confusing. That’s why Fleming Heating & Air Conditioning Inc professionals are here to help with a no-cost, no-pressure quote for furnace installation. We’ll assess your home, your heating requirements and your budget before helping you find the right solution. Contact us at (877) 389-2465 to get started today!
Request Service
Sidebar
Deals & Financing
Receive up to $2,000 in rebates
when you purchase the Lennox® Ultimate Comfort System OR qualified buyers make no payments, incur no interest for 12 months** when financing a new Lennox® system Redeem Offer Expires 11/30/2025Labor Warranty
Two-year labor warranty with purchase of furnace and air conditioning. Redeem Offer Expires 11/30/2025Redeem Offer
Your Promotional Selection Has Been Applied!
Coupon Popup
Request Service
Request Service
Why Choose Fleming?
- 24/7 Emergency Service
- Trusted Local Experts Since 1964
- NATE-Certified Technicians
- Certified Lennox Premier Dealer
- Affordable Maintenance Plans
- Easy Financing Options Available
- Over 20,000 Customers Serviced